Presented by Pacific Labeling & Integration
Marking the Difference: How CIJ, TIJ, DOD, Laser and Print-and-Apply Secure Compliance
Introduction
Every package that leaves a production line carries more than just a product. It carries a promise of safety, authenticity and trust. In today’s global marketplace, that promise is enforced by the codes, labels, and markings applied during production. Whether it is a 2D barcode on a pharmaceutical blister pack, an expiration date on a beverage can or a serialized shipping label on a logistics pallet, accuracy and reliability are non-negotiable.
At the same time, pressures on manufacturers are mounting. Production lines are moving faster, product mixes are expanding, and regulations are tightening. Mislabeling has become one of the leading causes of recalls, costing companies billions of dollars every year. Regulatory bodies such as the FDA, USDA, and European Commission are mandating clearer, more durable, and data rich codes, while retailers and supply chain partners expect full traceability.
Meeting these demands requires a toolkit of advanced technologies. Continuous inkjet (CIJ) provides speed and flexibility, thermal inkjet (TIJ) delivers high resolution and clean operation, drop on demand (DOD) enables bold case coding, laser and UV systems ensure permanence and tamper resistance and print-and-apply systems allow variable data and serialization at scale. Each technology has strengths and limitations, but when applied correctly, they secure compliance, build trust and protect brands.
The Regulatory Landscape: Why Every Mark Matters
- Food and Beverage: Strict requirements for batch codes, expiration dates, and allergen labeling. A single error can lead to costly recalls, fines and consumer safety risks.
- Pharmaceuticals: Serialization is mandatory under the FDA’s DSCSA and the EU Falsified Medicines Directive. Every unit must carry a unique, machine readable identifier.
- Consumer Goods and Retail: GS1’s “Sunrise 2027” initiative is accelerating the shift to 2D barcodes, which carry more data for compliance, logistics, and consumer engagement.
- Global Trade: Customs and export documentation increasingly rely on scannable codes for cross border validation and security.
Failure to meet these requirements does more than interrupt shipments—it damages consumer trust and brand reputation.

Technology Options for Compliance and Traceability
Continuous Inkjet (CIJ)
CIJ is a cornerstone for high speed lines. It propels tiny, electrically charged ink droplets toward the substrate in a continuous stream.
- Strengths: Works on curved, wet and non-porous surfaces. Handles high throughput with ease.
- Challenges: Requires solvents, frequent cleaning and careful maintenance. Ink and make up fluid costs can accumulate.
- Best Uses: Beverages, cans, extrusion products and high speed packaging where durability matters.

Thermal Inkjet (TIJ)
TIJ generates ink droplets using heat and vaporization. Compact cartridges make it operator friendly.
- Strengths: High resolution for crisp barcodes, small text and QR codes. Low maintenance. Clean, cartridge based system.
- Challenges: Best on porous or semi porous surfaces. Less effective on non porous packaging at high speed.
- Best Uses: Pharmaceuticals, retail cartons and applications requiring serialization or 2D barcodes.

Drop on Demand (DOD)
DOD expels ink only when required, using valve or piezoelectric technology.
- Strengths: Produces bold, large character marks. Good for corrugated shipping cases and secondary packaging.
- Challenges: Less precise for fine detail. Maintenance of valves and nozzles is critical.
- Best Uses: Case coding, pallet marking and warehouse traceability.

Laser and UV Coding
Laser systems mark by etching or ablating material, while UV lasers deliver high contrast without inks.
- Strengths: Permanent, tamper proof marks with minimal consumables. Excellent for anti counterfeit and high value goods.
- Challenges: High upfront cost. Safety considerations require shielding and training. Some substrates may not respond well.
- Best Uses: Pharmaceuticals, electronics, medical devices and products requiring long lasting or high security marks.

Print-and-Apply Labeling
Print and apply combines variable printing with automated label application.
- Strengths: On demand labels reduce pre printed inventory. Supports serialization, regional data and logistics compliance.
- Challenges: Slower than roll fed decorative labeling. Label jams and misfeeds can cause downtime.
- Best Uses: Pallets, cartons, logistics labels and compliance stickers requiring variable data.

Integration with Packaging Lines
Compliance cannot be achieved in isolation. Successful coding and labeling require system wide alignment:
- Conveyors: Stable handling ensures codes and labels are placed correctly without smudges or skewing.
- Case Tapers: Securely sealed cartons prevent label damage and keep compliance data intact.
- Inspection Systems: Vision cameras confirm barcode readability and label placement in real time.
- Software Integration: ERP and MES connectivity ensures codes match production records and regulatory databases.

Emerging Trends in Coding and Labeling
Widespread Adoption of 2D Barcodes
1D barcodes are being replaced by 2D codes such as QR and DataMatrix, which carry batch data, expiry dates, and serialization in a compact form. GS1’s Sunrise 2027 initiative is the driver of this change. Manufacturers must invest in coders that can print these codes at line speed and inspection systems that verify their readability.
Sustainability in Consumables and Materials
Environmental pressures are reshaping consumables. Low VOC inks, water-based formulations, recyclable adhesives and linerless pressure sensitive labels are gaining traction. These reduce waste and align with sustainability goals, but they also require operators to adjust for differences in adhesion, drying times, and material behavior.
Smart and Connected Packaging
Labels and codes are no longer passive. Embedded QR, NFC, and RFID technologies connect consumers to product data, loyalty programs or authenticity checks. They also support end to end traceability in supply chains. This trend requires closer integration between coders, labelers, and enterprise data systems.
Predictive Maintenance and Quality Monitoring
Sensors and software now allow predictive maintenance. Coders track nozzle health and ink pressure, while label applicators verify placement and quality. Data analytics alerts maintenance teams before problems cause downtime. This increases uptime, reduces waste and lowers compliance risk.
Hybrid Systems for Compliance and Branding
Hybrid approaches merge decoration and compliance. For example, print and apply systems can apply branded labels that already include serialized barcodes, while TIJ or laser coders can add variable data directly to decorative labels. This reduces equipment footprint and ensures that branding and compliance move in sync.
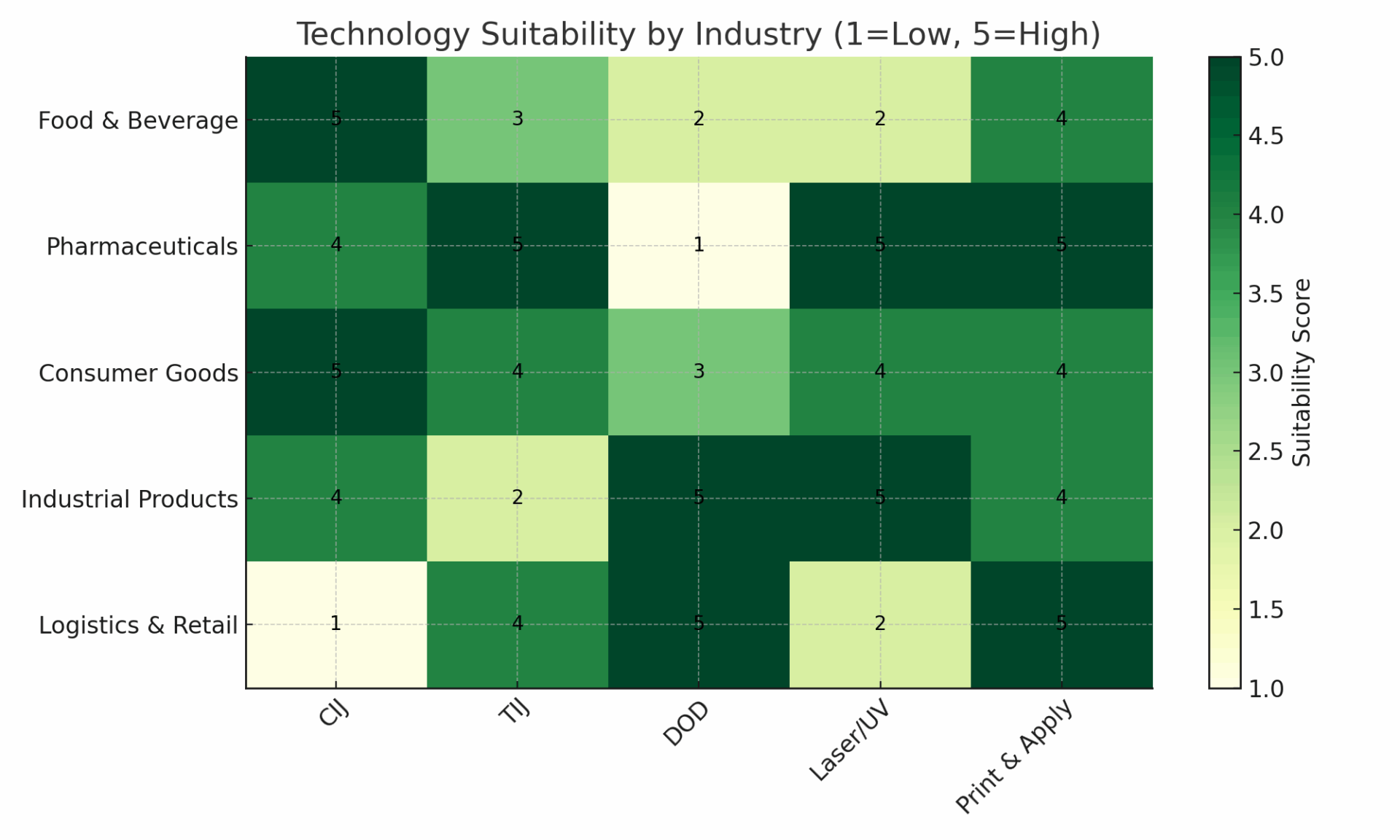
Industry Suitability Chart
Figure 1: Suitability of CIJ, TIJ, DOD, Laser/UV and Print & Apply technologies across key industries (1 = Low Fit, 5 = High Fit).
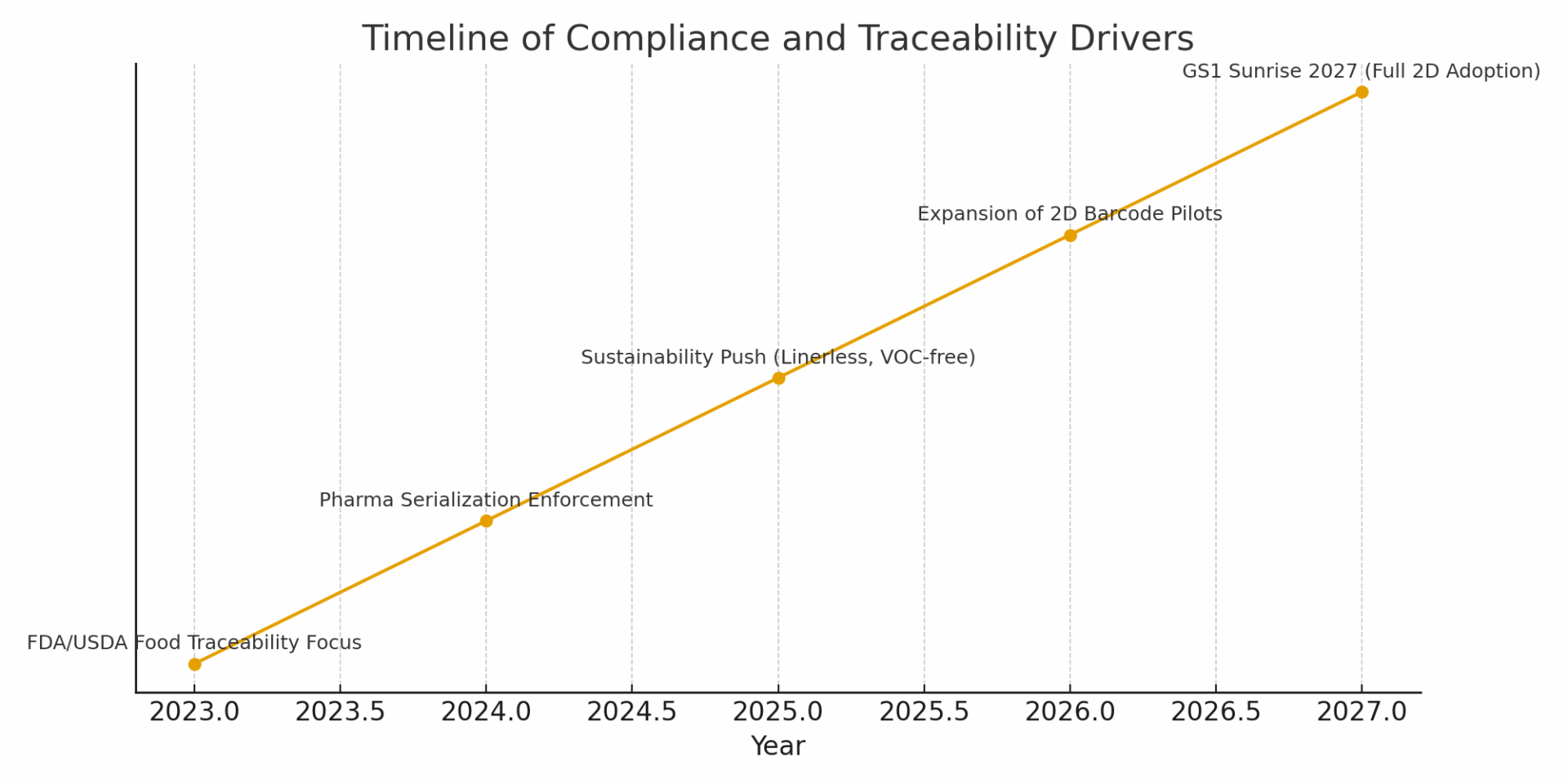
Compliance Drivers Timeline
Figure 2: Timeline of major compliance and traceability drivers leading up to GS1 Sunrise 2027.
Conclusion
Every mark on a package represents more than compliance. It represents consumer safety, brand trust and the integrity of global supply chains. CIJ, TIJ, DOD, laser/UV and print-and-apply systems are the backbone of that promise. Each technology has its place, and the right mix depends on line speed, product type, regulatory requirements and brand objectives.
For managers and engineers, the challenge is to weigh total cost of ownership against compliance risk. For maintenance teams, reliability and ease of service are critical. For marketing professionals, every code and label is part of the brand experience.
By embracing the right technologies and keeping pace with emerging trends, manufacturers can turn compliance into a competitive advantage while ensuring every package tells the right story from factory floor to consumer hands.
References
Food Marketing Institute. Cost of a Recall Report. FMI, 2023.
GS1 US. Sunrise 2027: The Move to 2D Barcodes. GS1, 2024.
Packaging World. Coding and Marking Trends at Pack Expo. Packaging World, 2024.
PMMI Business Intelligence. Trends in Packaging and Labeling Automation. PMMI, 2024.
Smithers Pira. The Future of Labels and Labeling to 2027. Smithers, 2023.
New Food Magazine. Label Errors Dominate 2024 US Food Recalls, Costing Industry $1.92 Billion. New Food Magazine, 2024.
Food Manufacturing. Reducing the Risk of Recalls. Food Manufacturing, 2023.
Packaging World. Innovative New Machinery at Pack Expo: Coding and Marking. Packaging World, 2024.


